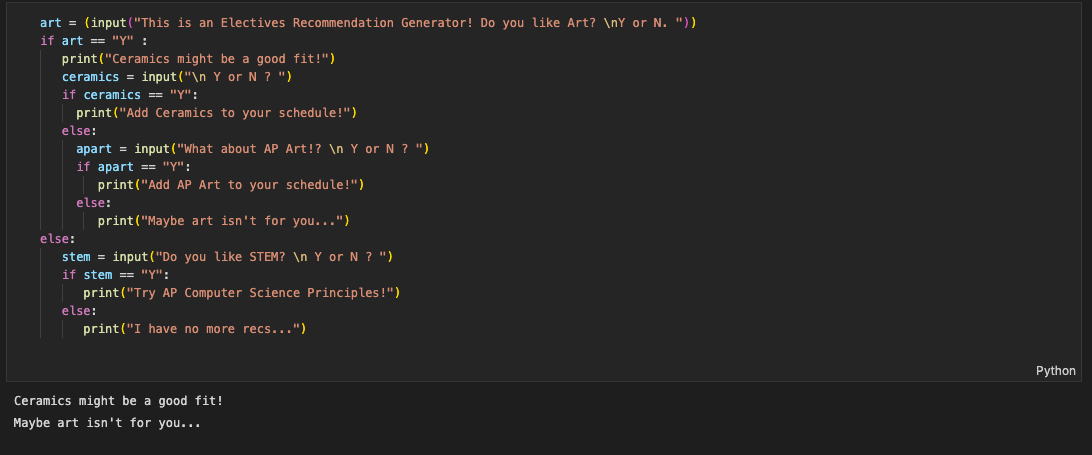
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Hacks
Unit 3.5-3.7 Hacks
Hacks 1 (3.5)
Boolean:
- A Boolean is a system of algebraic notation that represents logical propositions
- Booleans are also conditionals, testing whether a statement is true or false
Relational Operators:
- Mathematical relationships between variables
- EX: <, >, =
Logical Operators:
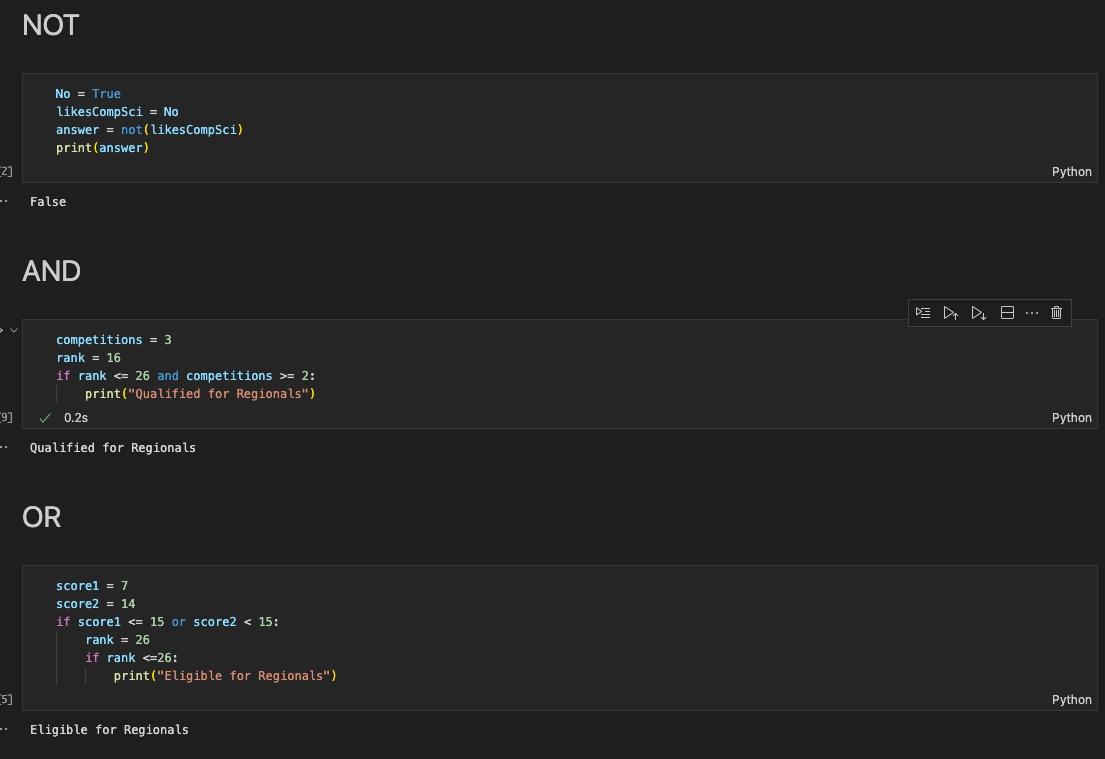
- NOT: displays opposite of data
- AND: evaluates two conditionals together
- OR: evaluates conditionals and if one is true then code will execute
NOT, AND, OR
Hack 2 (3.6)
Key Terms
Selection: Selection is the code that will execute depending on whether or not the conditional is true or false.
- EX: “print(“This is for APSCP”)” if a conditional was true would be the SELECTION part of code
Algorithm: An algorithm is the instructions for the code to execute
- EX: the code written below is an ALGORITHM
Conditional Statement / If-Statement: (Depends on boolean value) This statement determines whether or not the selected code will run. If the conditional is true, then the code will execute. If false, then it will not.
- EX: CONDITIONAL seen in code below (if test1 >= 75…)
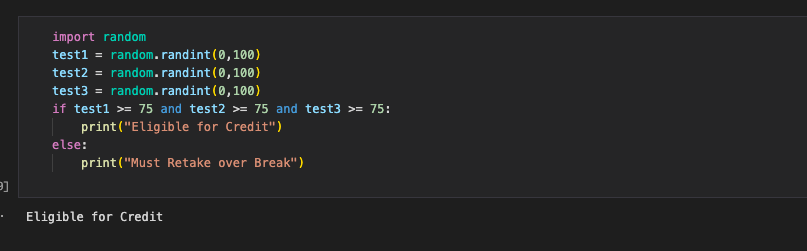
3.6 Hacks #1
- For the first hack, pretend you are a school’s test grader. Create an array with integers, each integer representing one score from a student’s taken tests. If the average of the student’s test scores are at least 75 percent, then display that the student is eligible for credit, and if not, display that the student must retake the tests over break.
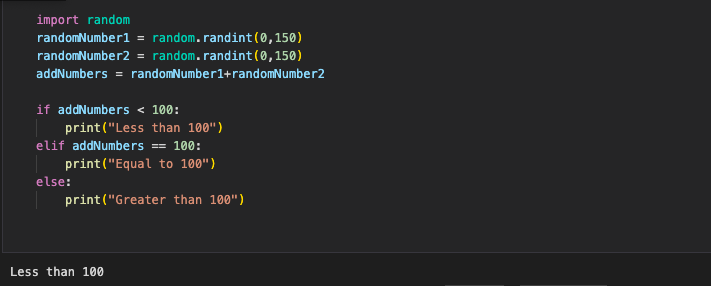
3.6 Hacks #2
- The second hack is more number-oriented. Create an algorithm that calculates the sum of two numbers, then determines whether the sum is greater than or less than 100.
Hack 3 (3.7)
Flow Chart and Code #1
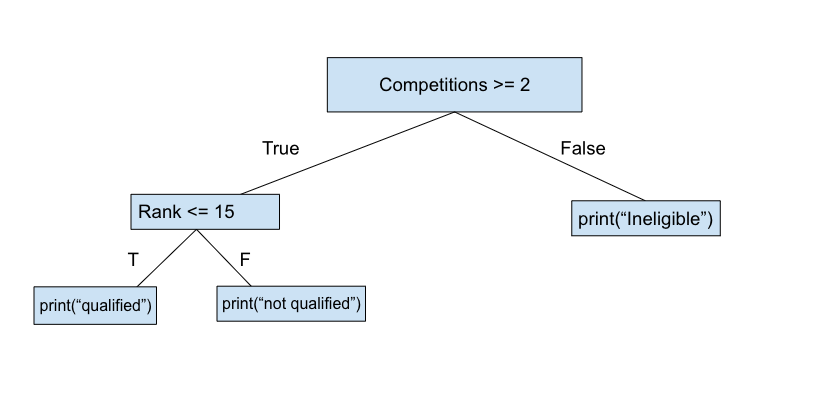
CODE
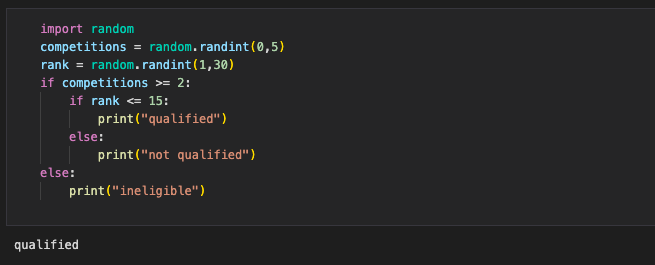
Flow Chart and Code #2
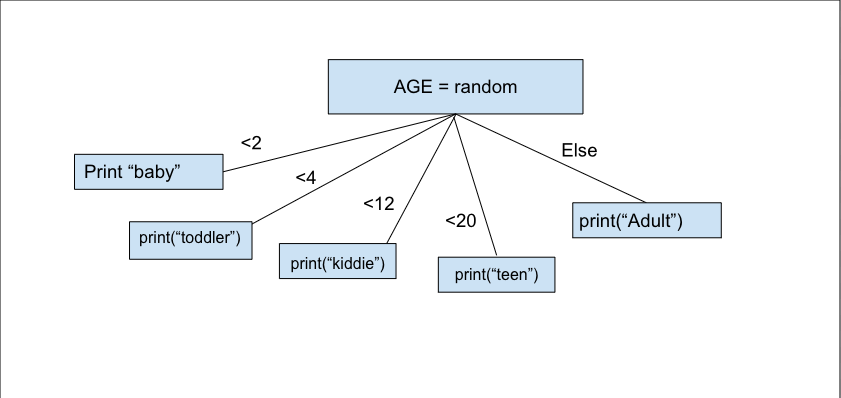
CODE
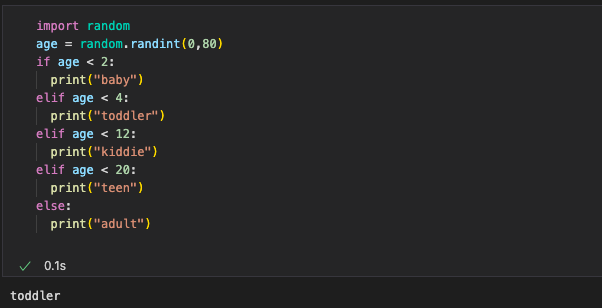
Flow Chart & Code #3
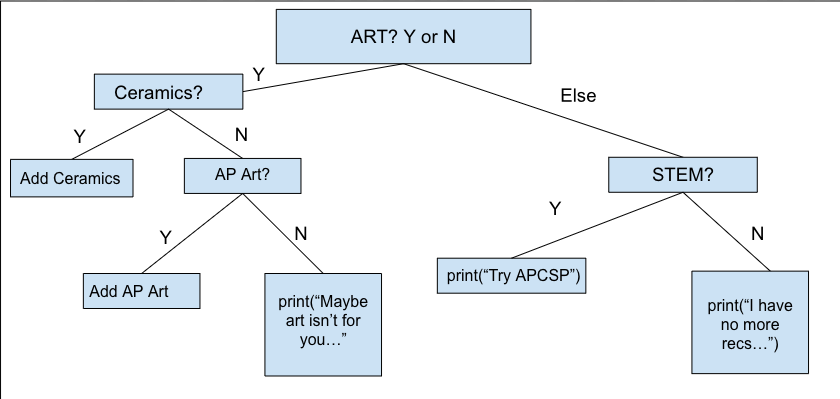
CODE