Unit 3 Lesson 4 Hacks
Unit 3 Section 8 and 10 Hacks
3.8.1 Hacks
Iteration:
An iteration is a repeating portion of an algorithm
- repeats a specified number of times or until a given condition is met
Iteration example
EX: Seeing which mailbox the key fits in
- m = number of mailboxes
- Mailbox number 1-m
- Try key in mailbox
- Try next mailbox (next highest)
- Repeat until key fits
- Get your mail!
STOPPING CONDITION: use “break” to stop the iteration
3.8.2
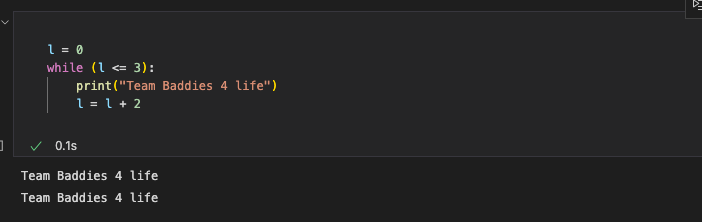
Iteration Statement:
Iteration statements repeat statements 0+ times (in a loop) until the conditional to break the look is met
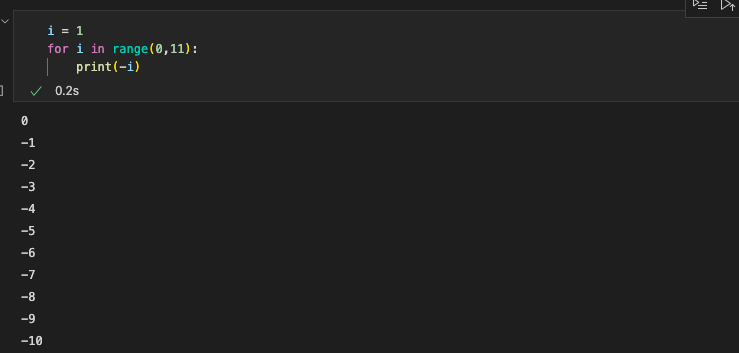
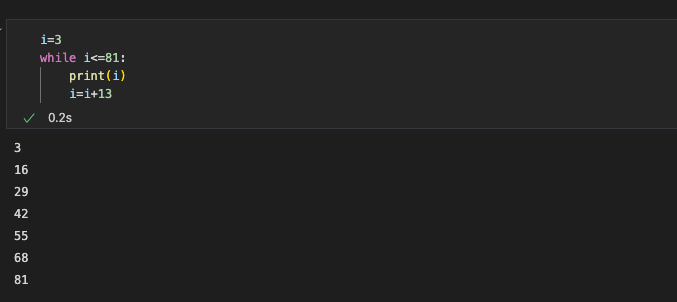
3.10 Hacks
Practice Problems
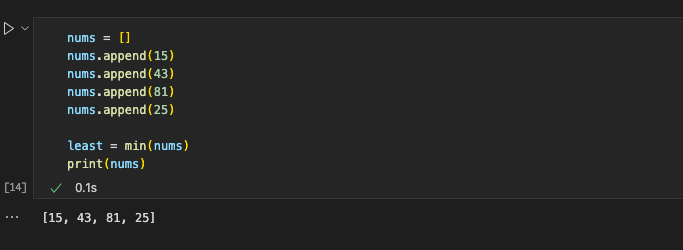
Hacks Part 1
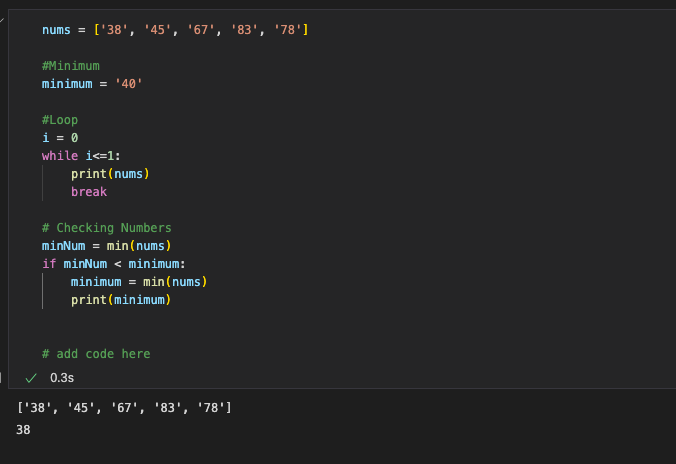
Hacks Part 2
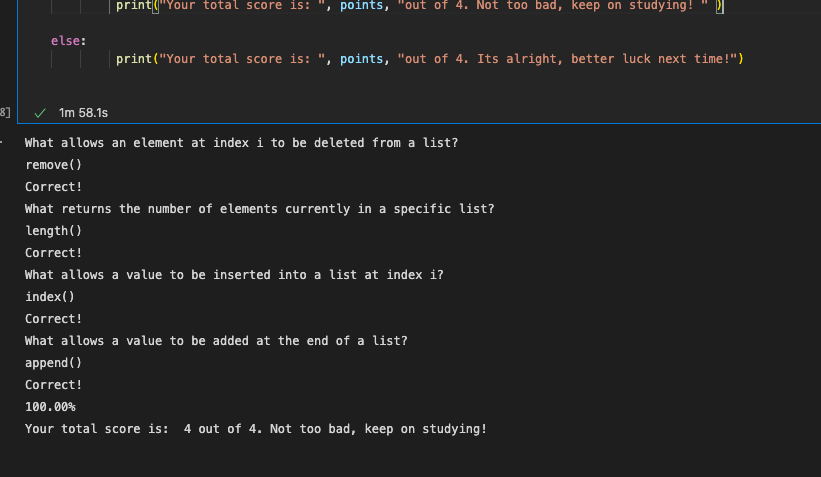
VOCAB:
- insert( ) allows a value to be inserted into a list at index i
- append( ) allows a value to be added at the end of a list
- remove( ) allows an element at index i to be deleted from a list
- length( ) returns the number of elements currently in a specific list
a <– EXPRESSION
- Moves whatever “expression” is into the variable “a”
LIST <– []
- Creates an empty list under the variable “LIST”
- Allows you to add elements via “append”
- Append is APPEND(LIST, x)
List[i]
- “i” is where you would access the list (EX: index[1])
LENGTH(list)
- Evaluates the number of elements in the list
Quiz Score